Cinnamon, derived from the inner bark of trees belonging to the genus Cinnamomum, is not just a flavorful addition to culinary dishes but also a spice packed with numerous health benefits. Used for centuries in traditional medicine, cinnamon offers a range of properties that can enhance overall well-being. This article delves into the various health benefits of cinnamon, highlighting why it deserves a place in your daily diet.

Cinnamon is a spice made from evergreen tree bark. There are two main types of cinnamon – Cassia and Ceylon. Cassia hails from China, Vietnam and Indonesia and is the most widely-used form of cinnamon in the US and Canada. While Ceylon is produced in Sri Lanka, India, Madagascar, Brazil and the Caribbean and is considered to be a ‘true’ form of cinnamon.
Origins and Cultivation
Cinnamon is a spice that comes from the inner bark of several species of evergreen trees (Cinnamomum), which belong to the laurel family.
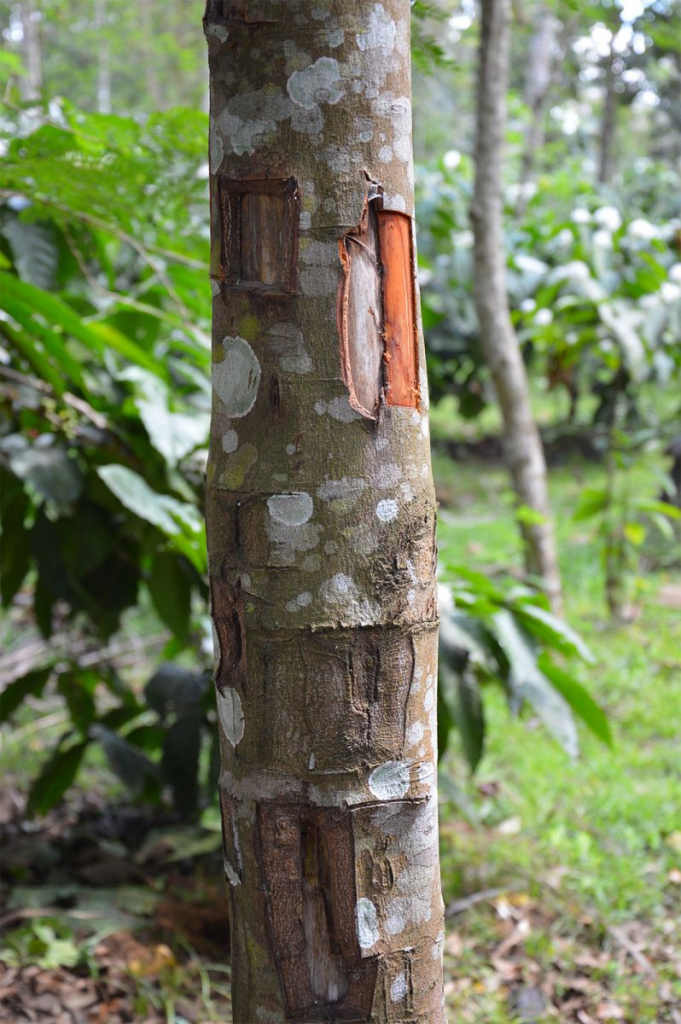

This spice is grown all over Asia, Europe, and North America, with the most popular varieties hailing from Sri Lanka and China. As for its historical roots, cinnamon was used by the ancient Egyptians together with myrrh to embalm the dead, and the Romans burned it on funeral pyres. It was used in religious ceremonies by the ancient Hebrews and is referenced in the Bible as a holy anointing oil ingredient.
There are two main types of cinnamon – Cassia cinnamon, which is produced in China, Vietnam and Indonesia, and is most commonly sold in the United States and Canada. And there’s Ceylon cinnamon, which is produced in Sri Lanka, India, Madagascar, Brazil and the Caribbean. It’s known as ‘true’ cinnamon and has more of a subtle flavour.
What are the benefits of cinnamon?
Rich in Antioxidants
Cinnamon is loaded with powerful antioxidants, such as polyphenols, which protect the body from oxidative damage caused by free radicals.
Benefits:
- Anti-Inflammatory Properties: The antioxidants in cinnamon help reduce inflammation, which can lower the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and arthritis.
- Cell Protection: By neutralizing free radicals, cinnamon can help protect cells from damage and reduce the risk of cancer.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
Chronic inflammation in the body can lead to various health problems. Cinnamon contains compounds that have potent anti-inflammatory effects.
Benefits:
- Pain Relief: Reducing inflammation can help alleviate pain and swelling associated with conditions like arthritis.
- Disease Prevention: Lowering chronic inflammation may reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease and neurodegenerative diseases.

Blood Sugar Regulation
One of the most well-known benefits of cinnamon is its ability to improve blood sugar control.
Benefits:
- Insulin Sensitivity: Cinnamon can enhance the sensitivity of insulin, a hormone crucial for blood sugar regulation, making it particularly beneficial for people with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
- Lower Blood Sugar Levels: Several studies have shown that cinnamon can lower fasting blood sugar levels and improve overall blood sugar control.
Antimicrobial Properties
Cinnamon has natural antimicrobial properties, making it effective against various types of bacteria, fungi, and viruses.
Benefits:
- Infection Prevention: Cinnamon can help prevent infections and may be effective in treating respiratory tract infections caused by fungi.
- Oral Health: The antimicrobial properties of cinnamon can help reduce bad breath and fight oral pathogens, promoting better oral health.
Heart Health
Cinnamon has several benefits that can promote heart health, making it a valuable addition to a heart-healthy diet.
Benefits:
- Cholesterol Levels: Studies suggest that cinnamon can reduce levels of total cholesterol, LDL (bad) cholesterol, and triglycerides, while maintaining stable HDL (good) cholesterol levels.
- Blood Pressure: Cinnamon has been shown to help reduce blood pressure, which is a significant risk factor for heart disease.
Neuroprotective Effects
Cinnamon contains compounds that may help protect the brain from age-related decline and neurodegenerative diseases.
Benefits:
- Cognitive Function: Regular consumption of cinnamon may improve cognitive function and reduce the risk of conditions like Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
- Memory Enhancement: Some studies suggest that cinnamon can enhance memory and learning capabilities.
Weight Management
Incorporating cinnamon into your diet can also aid in weight management.
Benefits:
- Metabolism Boost: The spice can increase metabolism, helping the body to burn fat more efficiently.
- Appetite Control: Cinnamon can help regulate appetite by stabilizing blood sugar levels, which can reduce cravings and prevent overeating.
Use of Cooking
There are several different ways to eat cinnamon sticks. You can grind them into a powder that you can then sprinkle on the top of cakes, desserts, biscuits and other dishes, or you can stir it into food as you’re cooking.

You can use cinnamon sticks in all sorts of ways when it comes to baking, cooking and making drinks. As for baking, you can take the sticks and crumble or grind them into a powder that can then be added to your cake, biscuit or other dessert recipes. Or you can almost use the powder as a garnish and sprinkle it over your bakes for an extra bit of flavour and final extra touch.
Another idea you may want to try is taking a couple of cinnamon sticks and adding them whole to servings of ice cream or similar. And if you’re baking anything with a sugar coating, e.g. doughnuts, why not add some crumbled up cinnamon sticks to your sugary topping too?

Cinnamon is a versatile spice that offers a myriad of health benefits, from its rich antioxidant content to its ability to regulate blood sugar and improve heart health. By incorporating cinnamon into your daily diet, you can enhance your overall well-being and protect against a variety of chronic conditions. Whether you sprinkle it on your oatmeal, add it to your coffee, or use it in savory dishes, the health benefits of cinnamon make it a worthy addition to your culinary repertoire.


